Movement
Presage Movements
Watches of today contain many technologies that were first developed by Seiko or technologies that are unique to Seiko.
Presage has inherited over 100 years of watchmaking tradition, and ingenuity and ideas continue to be added to it to evolve it further.
- The technologies adopted in each model differ.

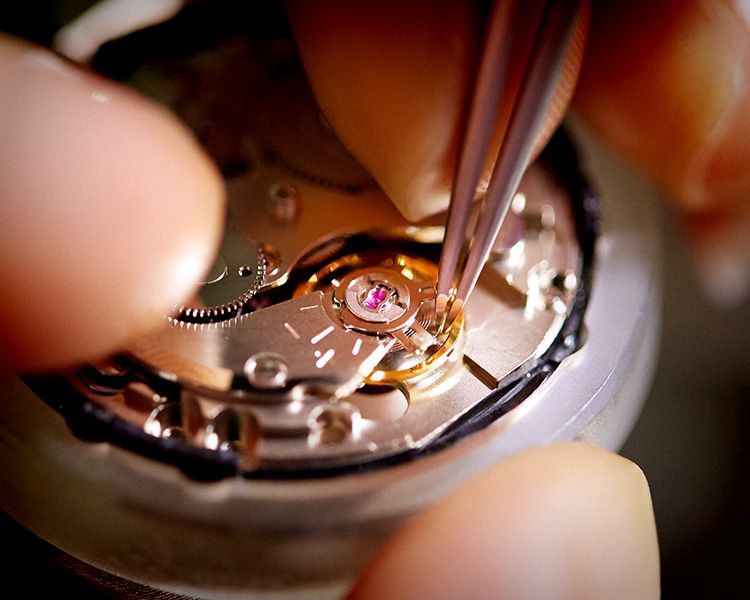
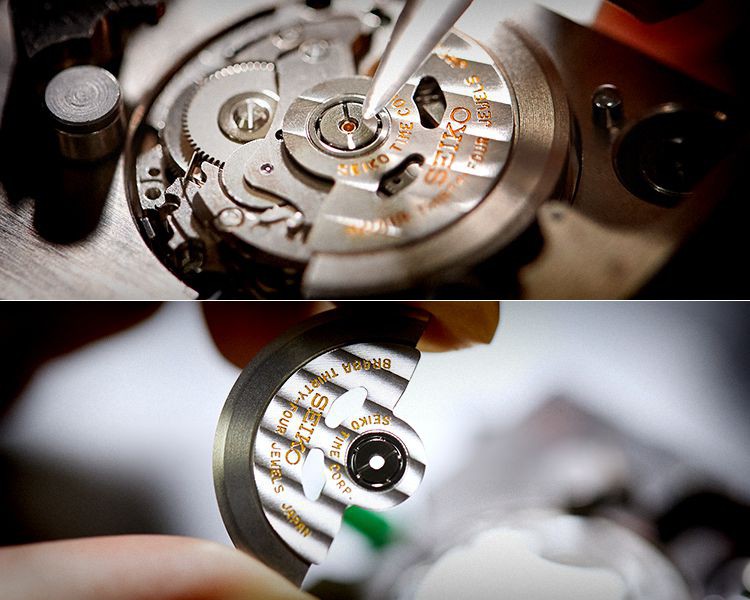
Mechanical
Mechanical watches move their hands by using a spring as a power source. They achieve the function of displaying the time by mechanical means only, with no electric controls.
TRIMATIC
TRIMATIC refers to three proprietary technologies developed by Seiko to make mechanical watches easy to use in daily life and precise over a long period. These structures, parts, and materials, named Diashock, Magic Lever, and Spron, respectively, are supported by innovation and tradition and are used in many models of Presage.
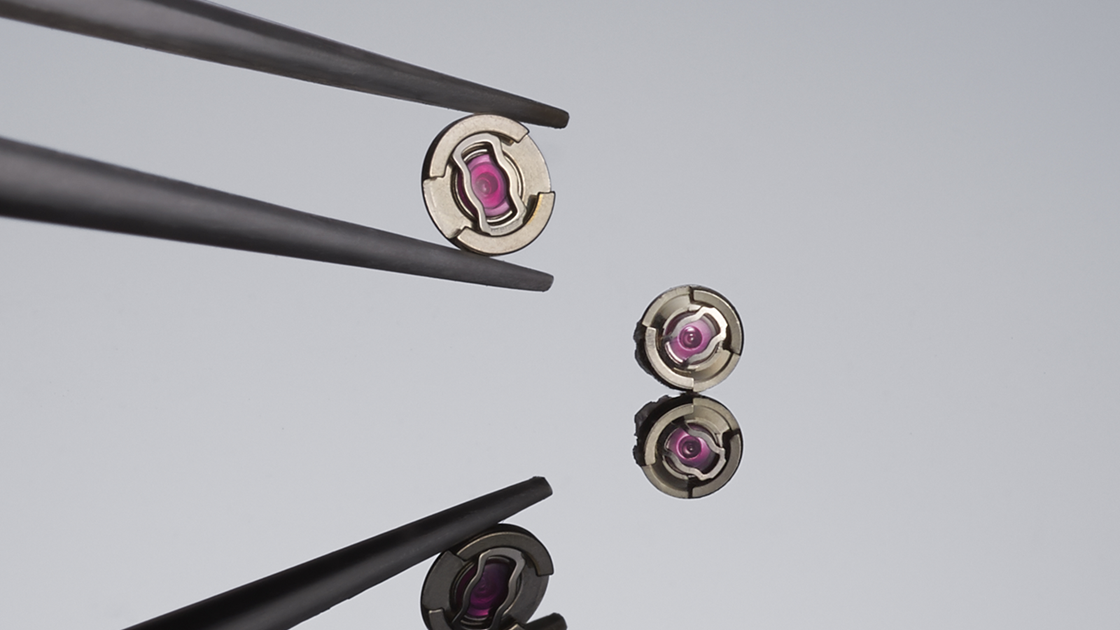

Diashock
Diashock is a structure developed to enhance shock resistance. It is used in the movement of a mechanical watch as a bearing, such as for the balance wheel pivot, which is especially sensitive to shocks and vibration. The structure maintains high stability even when sudden shock is applied.
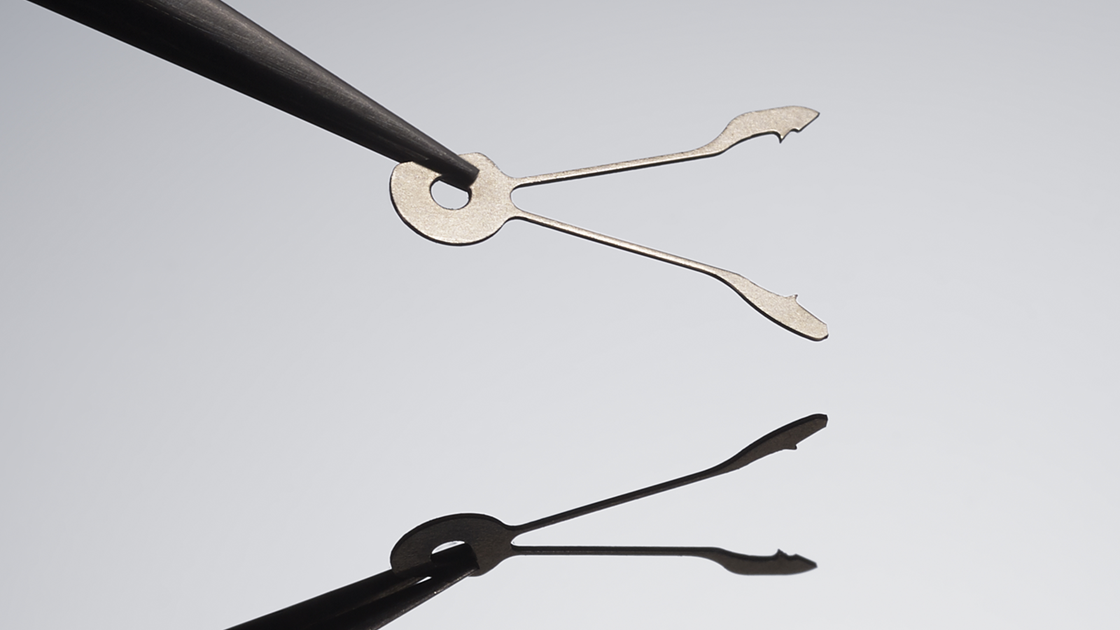
Magic Lever
The Magic Lever has the important role of efficiently winding the mainspring in an automatic movement. It has two spring pullets of different shapes that are always in contact with the transmission wheel used to rotate the barrel. Regardless of the rotational direction of the rotor, the two pullets of the Magic Lever always generate a unidirectional movement of the transmission wheel enabling efficient winding of the mainspring.
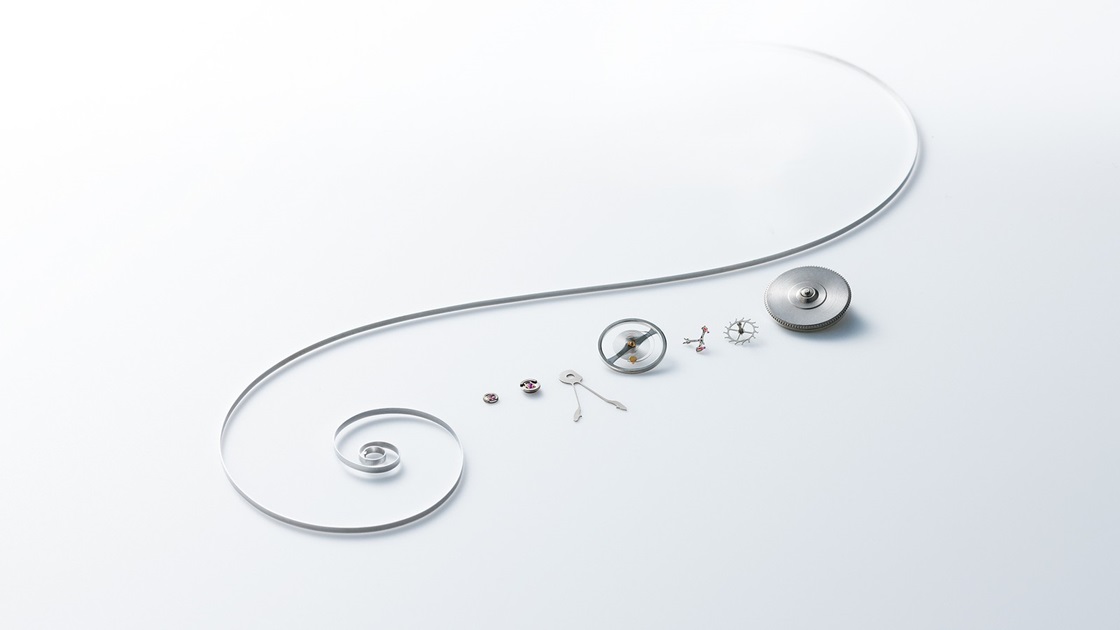


SPRON
Spron is an alloy material developed with the aim of being resistant to tear, corrosion and ware to make mechanical watches that can be used over a long period of time, Seiko has worked on the development and manufacturing of springs for more than half a century, and it has adopted its proprietary material Spron to be applied for the mainspring and hairspring.
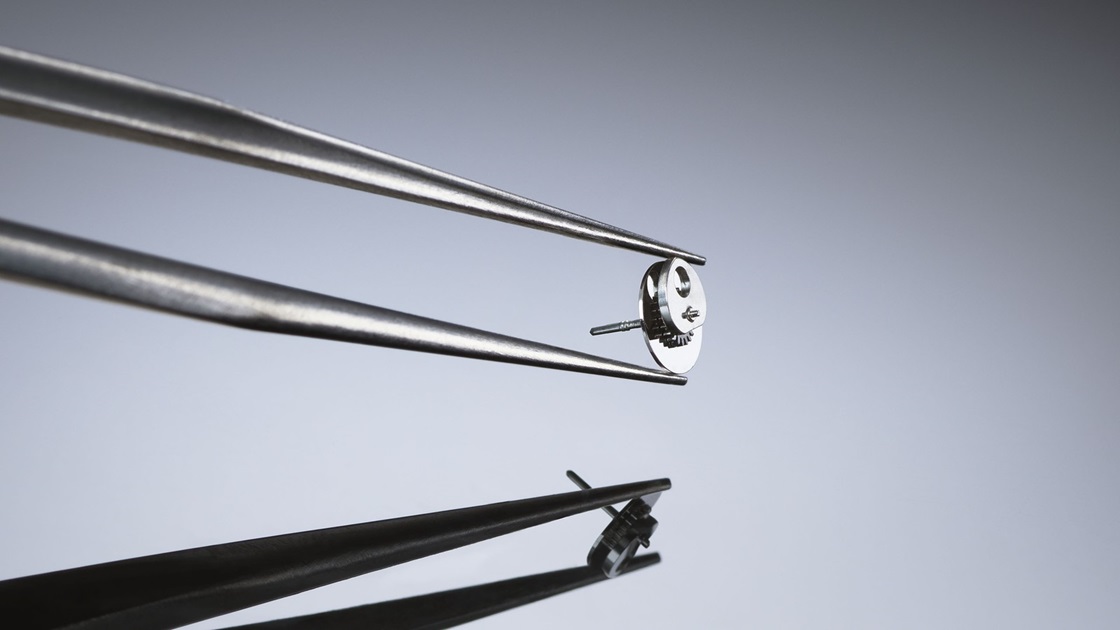
Vertical clutch
Stopwatch features that boast precise operation
Caliber 8R48, adopted by Presage, uses a column wheel* and vertical clutch in the operational systems for the stopwatch, which can be said to be a feature of a high-end chronograph. The vertical clutch is a system that was first developed by Seiko in 1969. It is a power transmission system with little hand skipping when it starts and stops and has excellent shock resistance.In addition, it is equipped with a proprietary three-pointed hammer that resets multiple hands realizing precise operation and excellent durability.
- A column wheel is a gear used to control the stopwatch.
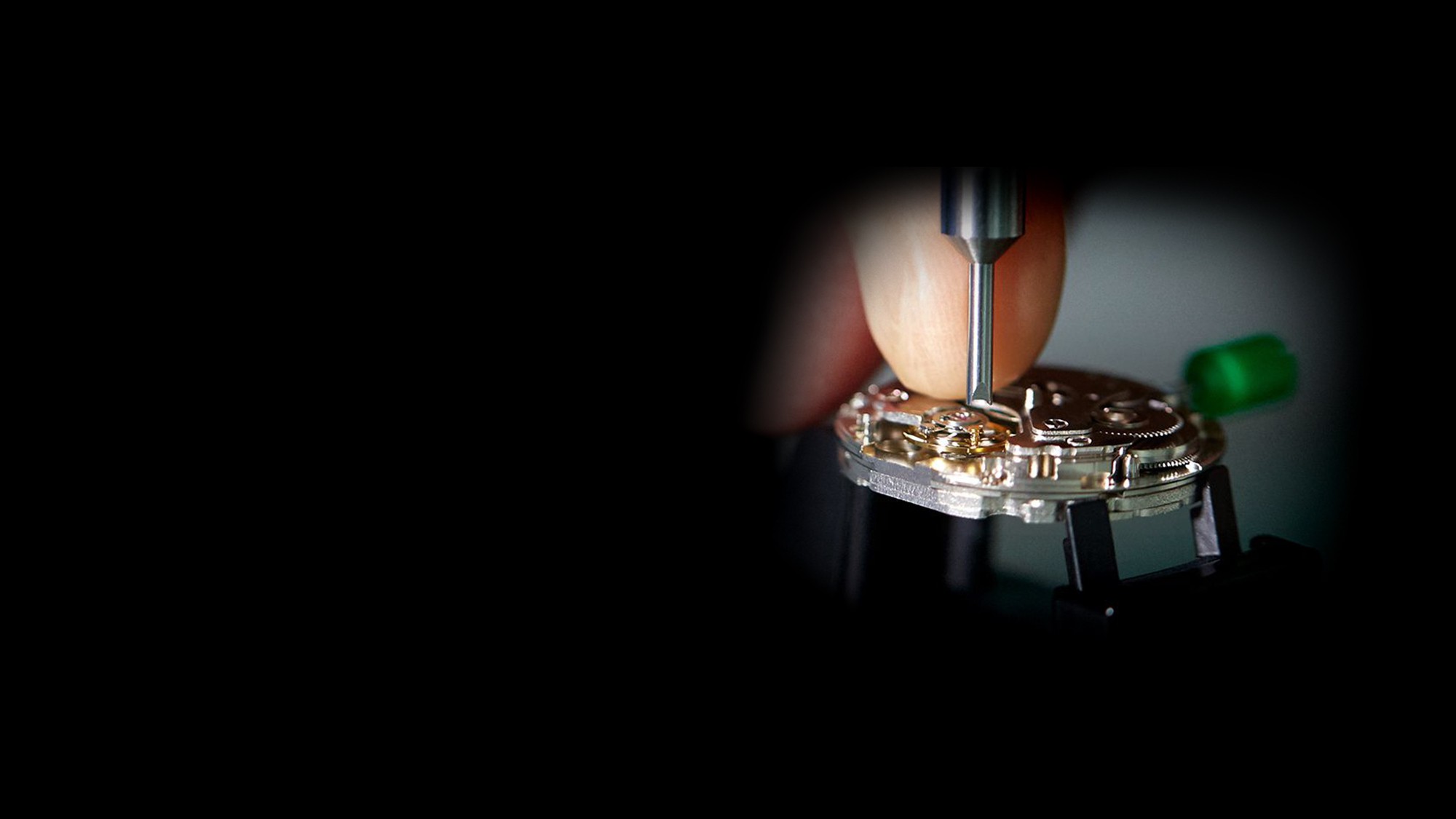


Design, Assembly, and Inspection
Seiko has over 100 years of watchmaking heritage, and continues to work on enhancing its watchmaking techniques and skills.
Through rigorous inspections, features such as water resistance, and functions such as chronographs, as well as appearance, precision, dirt and lint contamination, and rotation of hands are checked, and only those products that meet Seiko’s standards are accepted.